General Description
ALLN is a cell permeable reversible inhibitor of Calpain 1 (calpain I, Ki = 190 nM), Calpain 2 (calpain II, Ki = 220 nM), cathepsin B (Ki = 150 nM), and cathepsin L (Ki = 500 pM). Calpains and cathepsins have been found to be involved in various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and programmed cell death, commonly known as apoptosis.
It inhibits neutral cysteine proteases and proteasome (Ki = 6 μM). It inhibits dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in thymocytes and cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in metamyelocytes. It also inhibits cell cycle progression at the G1/S border and metaphase/anaphase in CHO cells by inhibiting cyclin B degradation. ALLN inhibits the proteolysis of IκBα and IκBβ by the ubiquitin-proteasome complex. Furthermore, it protects against neuronal damage caused by hypoxia and ischemia. ALLN also prevents LPS associated nitric oxide synthase production by activated macrophages by interfering with transcription of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Calpain Inhibitor I inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced (TNF-induced) cleavage of Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and calpastatin in apoptosis. It also inhibits oxygen/glucose deprivation (OGD) induced cleavage of caspase-12 and Bcl-xL.
Applications:
Calpain Inhibitor I has been used:
- as a component of protease inhibitor cocktail for gel shift analysis
- for treating HeLa cell cultures
- for inhibition of 26 S proteasome in 26 S proteasome inhibition assays
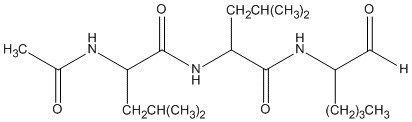
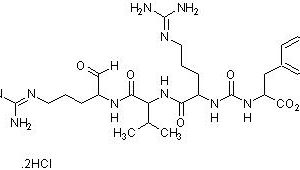
Molecular Formula: C20H37N3O4
Molecular Weight: 383.53








![IEF Anode Buffer [50X]](https://www.cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10496-3-430x334.jpg)
![IEF Cathode Buffer (pH 3-7) [10X]](https://www.cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10498-3-430x334.jpg)