General Description
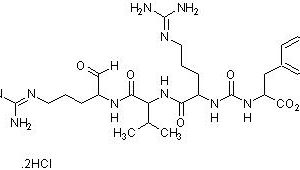
A polypeptide, present naturally in blood and in most tissues, with a high concentration in the lung. Aprotinin is a serine protease inhibitor and inhibits a wide range of proteases that include
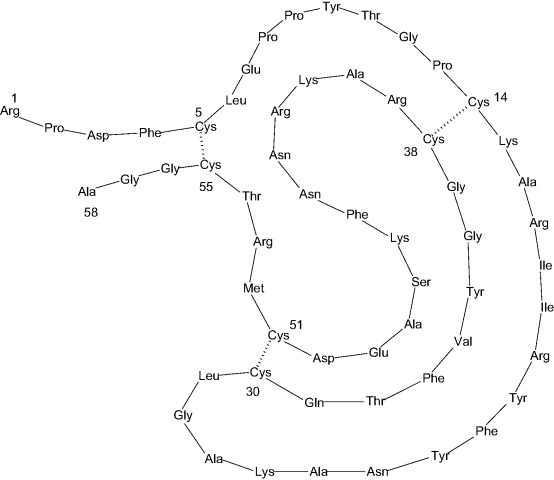
trypsin, chymotrypsin, kallikrein and plasmin with a weak inhibition of trypsinogen and thrombin. It is typically used as a protease inhibitor to prevent degradation of proteins by active proteases in the protein sample preparations. Aprotinin contains a single peptide chain with three disulfide bonds.
Aprotinin is a competitive serine protease inhibitor which forms stable complexes with and blocks the active sites of enzymes. The binding is reversible, and most aprotinin-protease complexes dissociate at pH >10 or <3.2.
Aprotinin is freely soluble in water (>10 mg/mL) and in aqueous buffers of low ionic strengths. Dilute solutions are generally less stable than concentrated ones. Solution stability also depends on pH; values of 1-12 can be tolerated. Repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided.
Applications
• Protein purification
• Used to preserve biological fluids, cells, and tissues from proteolytic damage
Molecular Weight: ~ 6511.




![IEF Anode Buffer [50X]](https://www.cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10496-3-430x334.jpg)