General Description
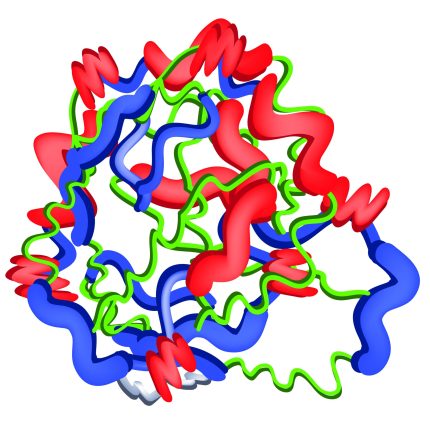
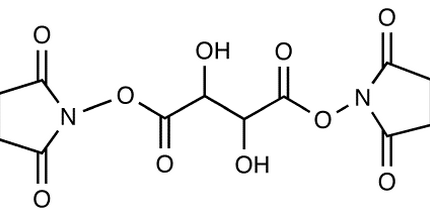
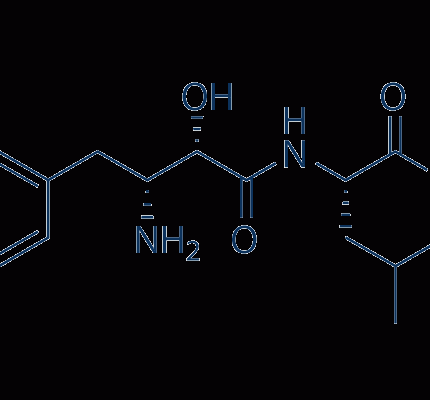
Avidin is a homotetrameric glycoprotein obtained from egg whites with a molecular weight of 68kDa and holds four identical subunits with each subunit containing 128 amino acid residues with a variable carbohydrate moiety. Each subunit has a single biotin binding domain. It is a basic protein with an isoelectric pH of 10-10.5 and is readily soluble in aqueous buffers containing a wide range of salt, pH, temperature and other laboratory agents. The binding affinity of avidin to biotin is very high, thus, is used to label antibodies, fluorescent dyes, proteins, and other molecules of interest to biochemists. Avidin and biotin are also incorporated into immobilized matrices. The avidin-biotin system has been utilized to link proteins in immunoassays to detect the localization of antigens in tissues by exploiting the very high affinity of avidin for biotin. The use of avidin-biotin immunoassay enhances the sensitivity of the technique and facilitates the detection of antigens in low quantities.
Application:
- Avidin egg white was used in an assay using functionalized xenon as a biosensor to detect biotin-avidin binding. Egg white was used at 80 nmol concentration.
- Egg white avidin has been used as a cross-linker for biotin-conjugated antibodies. The product has also been used as a blocking agent in ELISA applications.