General Description
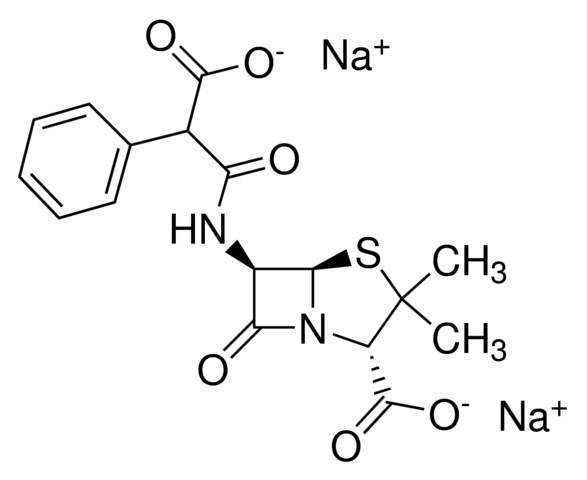
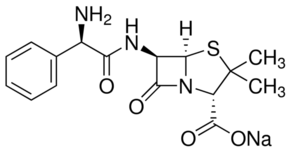
Carbenicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, which inhibits bacterial cell-wall synthesis (peptidoglycan cross-linking) by inactivating transpeptidases on the inner surface of the bacterial cell membrane. It is semi-synthetic penicillin antibiotic with bactericidal and beta-lactamase resistant activity. It acylates the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase C-terminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This inactivation prevents the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan strands, thereby inhibiting the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. This leads to incomplete bacterial cell wall synthesis and eventually causes cell lysis.
Synonyms: Carbenicillin sodium, Carbecin, Sodium carbenicillin, Carbenicillin, Carboxybenzyl Penicillin, Disodium Carbenicillin, Geopen, Microcillin, Pyopen, Carbapen
CAS Number: 4800-94-6;
Molecular Formula: C17H16N2Na2O6S
Molecular Weight: 422.363
Features:
1. Used for selection of ampr transformed cells.
2. Used to study the role of penicillin-sensitive transpeptidases in cell wall biosynthesis.
3. Antimicrobial spectrum: Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, Pseudomonas.




![SSC [20X]; Sodium Chloride-Sodium Citrate (0.3M sodium citrate](https://www.cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10411-SSC-10X-500-ml-scaled-430x430.jpg)

