General Description
Chymostatin is strong inhibitor of many proteases including chymases, chymotrypsin, papain, chymotrypsin-like serine proteases, and lysosomal cysteine proteases, such as cathepsins A,B,C, B, H, and L. It weakly inhibits human leucocyte elastase. It is effective at a final concentration of 100 to 200 μg/ml (10 to 100 μM) and is often included as an integral component in the protease inhibitor cocktails used with plant extracts.
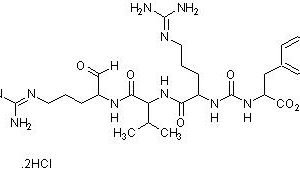
Chymostatin consists of three major components; A, B, and C, where A being N-[((S)-1-carboxy-2-phenylethyl)-carbamoyl]-α-[2-iminohexahydro-4(S)-pyrimidyl]-L-glycyl-L-leucyl-phenylalaninal, is the main component of this inhibitor. The other two components B and C differ in that the L-leucyl residue is substituted by L-valine and L-isoleucine, respectively.
Application:
Chymostatin is a specific inhibitor of α-, β-, γ-, and δ-chymotrypsin.
Synonym: N-(Nα-Carbonyl-Cpd-X-Phe-al)-Phe (Cpd = capreomycidine) (capreomycidine = [S,S]-α-(2-Iminohexahydro-4-pyrimidyl)glycine)
Solubility: DMSO
Storage: -20 °C






![IEF Cathode Buffer (pH 3-7) [10X]](https://cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10498-3-430x334.jpg)


