General Description
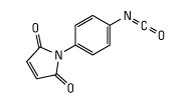
EDC is a water-soluble carbodiimide is a zero-length crosslinking agent used to couple carboxyl groups to primary amines, a crosslinker that activates carboxyl groups for spontaneous reaction with primary amines, enabling peptide immobilization and hapten-carrier protein conjugation. In addition, it reacts with phosphate groups. EDC has been used in peptide synthesis; crosslinking proteins to nucleic acids; and preparation of immunoconjugates as examples. Typically, EDC is utilized in the pH range 4.0-6.0 without buffers. In particular, amine and carboxylate buffers should be avoided.
Molecular formula: C8H17N3·HCl
Molecular weight: 191.70
Spacer arm length: 0 Å
CAS Number: 25952-53-8
Synonyms: N-Ethyl-N′-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDAC, EDC hydrochloride, EDC, WSC hydrochloride
Solubility: 100 mg/ml in water
Storage: -20°C. Protect from moisture. Shipped at ambient temperature.
Features of EDC:
• Reactive group: Carbodiimide
• Reaction target: activates carboxyl groups to conjugate to amino groups (primary amines)
• Conjugation strategies—react EDC alone with target groups or include NHS/Sulfo-NHS to increase reaction efficiency or to stabilize active intermediate for later
• Neutral linkage—forms neutral amide bonds between carboxyls and amines
• Water-soluble reagent—add directly to reactions in aqueous, physiological buffers
• Soluble reaction byproducts—easily removed by washing with water or dilute acid
• High-purity, crystalline reagent—use to create high-quality, activated derivatives
Applications:
• Conjugate carboxyl and amino groups among peptides and proteins
• Couple haptens to immunogenic carrier proteins
• Create NHS-activated, amine-reactive labeling compounds
• Crosslink proteins to carboxyl coated beads or surfaces
• Activate nanoparticles with amine-reactive Sulfo-NHS esters
• DNA labeling through 5′-phosphate groups



![EDC (1-Ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride) EDC (1-Ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride)](https://www.cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10539-1.png)



![IEF Anode Buffer [50X]](https://www.cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10496-3-430x334.jpg)