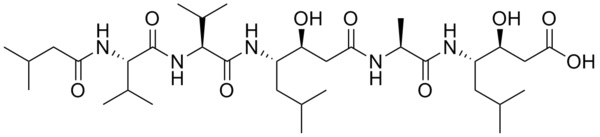
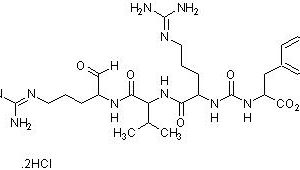
Pepstatin A is a pentapeptide and was originally isolated from microbes. It is a highly effective reversible, competitive inhibitor of aspartyl proteases and uniquely contains an unusual amino acid statine, that is active against acid proteases such as pepsin, chymosin, renin and cathepsins D & E. It has IC50 values of 15 μM, 2 μM, <5 nM and <40 nM for human renin, HIV protease, pepsin and cathepsin D, respectively [1, 2]. It is a highly selective protease inhibitor and in vitro studies have shown that this is the only aspartic acid inhibitor that inhibits HIV proteases and has been used to better understand the mechanisms of HIV-infected cells. It does not inhibit thiol proteases, neutral proteases, or serine proteases, but helps prevent the degradation of hemoglobin. It is practically insoluble in water and ether, but can be dissolves in ethanol.
Molecular Formula: C34H63N5O9
Molecular Weight: 685.89
CAS No.: 26305-03-3
Appearance: White powder
Solubility: In Ethanol: soluble1-2 mg/mL
Storage: 2 to 8°C
References:
1. Eid M, Evin G, Castro B, et al.New renin inhibitors homologous with pepstatin.Biochem. J, 1981, 197: 465-471.
2. Sarubbi E, Seneci P F, Angelastro M R, et al. Peptide aldehydes as inhibitors of HIV protease. FEBS letters, 1993, 319(3): 253-256.







![IEF Cathode Buffer (pH 3-7) [10X]](https://www.cephamls.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/10498-3-430x334.jpg)