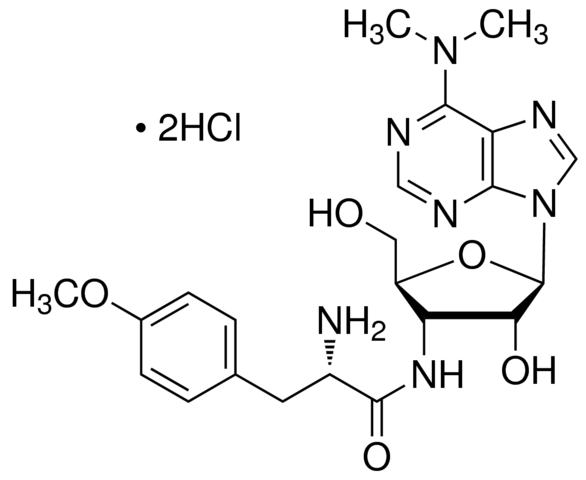
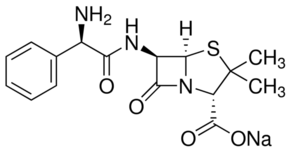
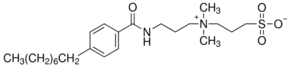
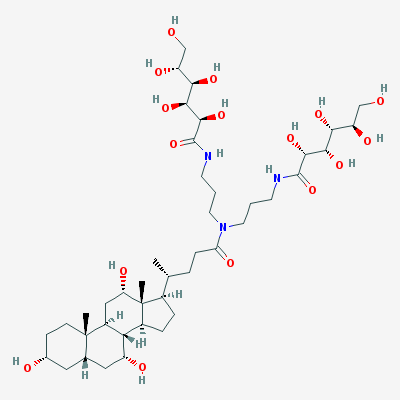
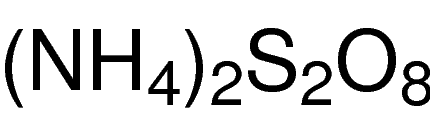Puromycin associates in a non-specific manner with growing polypeptide chains, and thus, leads to premature termination of translation. It inhibits protein synthesis in two ways. It associates with the donor substrate, peptidyl-tRNA, in the P site and thus, functions as an acceptor substrate. Second, it competes with aminoacyl tRNA to bind with the A′ site within the peptidyl transferase center.
Mode of Action: Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by causing premature chain termination acting as an analog of the 3′-terminal end of the aminoacyl-tRNA.
Mode of Resistance: Puromycin acetyltransferase is an effective resistance gene.
Antimicrobial Spectrum: This product is active against gram-positive microorganisms, less active against acid-fast bacilli and more weakly active against gram-negative microorganisms. Puromycin can prevent growth of bacteria, protozoa, algae and mammalian cells and acts quickly, killing 99% of cells within 2 days.